
For decades, researchers and have come to trust the DayStar Filters’ name for an industry standard in space flown narrow bandpass filters.
DayStar Filters is proud to have participated in a number of scientific investigations that have travelled beyond our planet. Working in close cooperation with mission teams, we delivered filters that performed to specifications, enabling mission success.
The DayStar solid state Fabry Perot Etalon crystal design is structurally robust and mechanically dependable, offering consistant tuning and on band performance
. Minimal considerations are required for adaptation to space-borne missions.
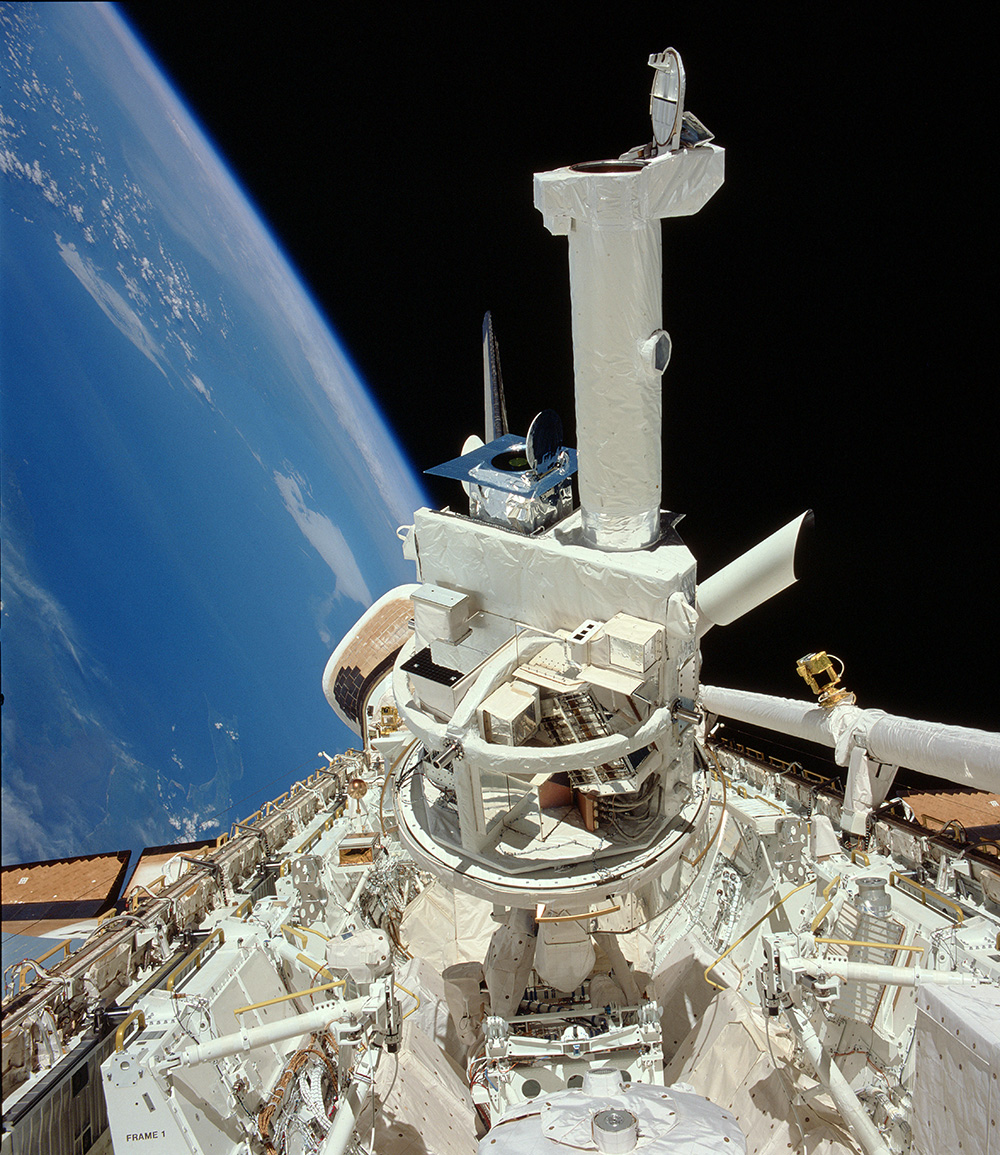
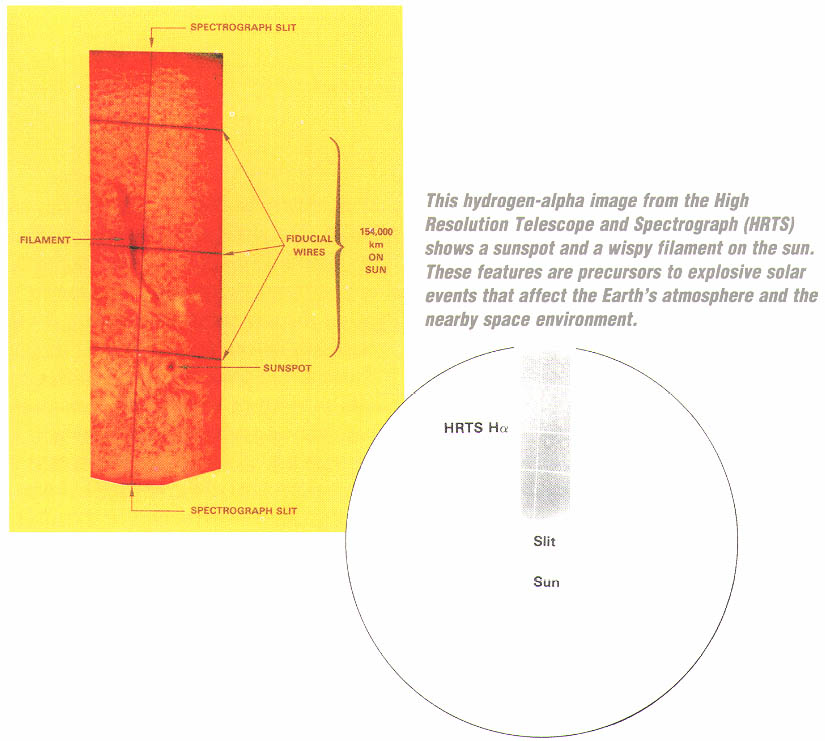
High Resolution Telescope and Spectrograph
Launch dates: 8 launches, 1983-1997
Launch Vehicles: Space Shuttle Challenger mission STS-51F; Black Brant 5C, Black Brant 9 suborbital sounding rockets
DayStar product: ruggedized 0.5Å two cavity Hydrogen Alpha filter, 60mm diameter, and 0.6Å Hydrogen Alpha filter, 50mm diameter.
The High Resolution Telescope and Spectrograph (HRTS) was launched numerous times to observe the Sun in ultraviolet light. Light reflected off the spectrograph slit jaws was passed through the DayStar filter to allow real time imaging and pointing of the telescope.

Normal Incidence X-Ray Telescope
Launch dates: 6 launches, 1986-1993
Launch Vehicle: Black Brant 8C and Black Brant 9 suborbital sounding rockets
DayStar product: 0.6Å Hydrogen Alpha filter, ATM housing.
The Normal Incidence X-Ray Telescope (NIXT) telescope incorporated a Hydrogen Alpha guide telescope that allowed real time pointing and control of the main X-ray telescope during the mission. Using an off-the-shelf ATM filter housing allowed costs to be kept to an absolute minimum with no sacrifice in performance. The mission gathered important scientific data and space-qualified the normal incidence technique later used by the SOHO, TRACE, and STEREO missions.

Tuneable XUV Imager
Launch dates: 2 launches, 2000-2001
Launch Vehicle: Black Brant 9 suborbital sounding rocket
DayStar product: 0.6Å Hydrogen Alpha filter, 25mm clear aperture.
The NIXT H-alpha camera design was used in the Tunable XUV Imager (TXI), for real time pointing control of the main extreme ultraviolet telescope. Using a 713mm EFL telephoto lens and Sony video camera resulted in a compact and simple instrument. Unfortunately, upon return of the 2001 flight the parachute failed to deploy, preventing any further flights. The DayStar filter, whose core element is a mineral crystal, was unharmed and could have flown again.
High Resolution Coronal Imager

White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico July 11, 2012:
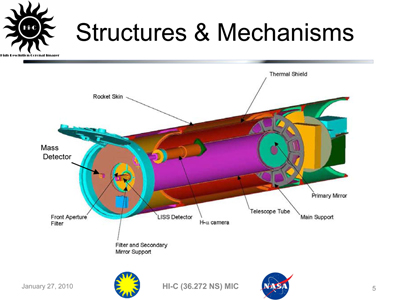
NASA’s High Resolution Coronal Imager, or Hi-C, captured the highest-resolution images ever taken of the sun’s corona in the extreme ultraviolet wavelength. Onboard, was also a DayStar Filters custom fabricated Hydrogen Alpha filter used for Hydrogen alpha comparison images and for pointing purposes.
DayStar provided support services of the project in cooperation with the Harvard Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. DayStar has produced several of such filters in the past, used on the Space Shuttle Challenger mission STS-51F as well as 9 previous suborbital Black Brant sounding rocket missions.
A standard DayStar Filters Quantum filter was initially produced for the project and used in planning stages and construction of the optical instrumentation package.
After optical qualification and fitting, the standard Quantum filter optics were moved to a space flight qualified housing. This would allow the housing to maintain temperature of the optical assembly throughout the ~900 second mission.
The ruggedized housing was designed to withstand liftoff vibration conditions; vacuum conditions and exposure to cosmic radiation present outside of Earth’s protective atmosphere. NASA provided test services for qualification of liftoff vibration conditions and vacuum chamber operations.

Hydrogen Alpha wavelength observations were not the primary focus of the investigations conducted by the Hi C, High Resolution Coronal Imager, but rather as an additional data reference.
“We will start acquiring data at 69 seconds after launch, at a rate of roughly an image a second,” says Jonathan Cirtain, a solar scientist at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. who is the project scientist for HI-C. “We will be able to look through a secondary H-alpha telescope on the instrument in real time and re-point the main telescope as needed.”
After the sucessful launch and mission of the
Hi C High Resolution Coronal Imaging mission, the capsule returned to earth and was recovered with optical instrumentation intact.

BOSCO II
Ground based solar filters were used to image supersonic jet aircraft passing in front of the Sun in order to use Schlieren photography to directly image the shock waves.
Reference: 1

International Space Station
We can’t discuss a mission currently in progress, other than to point out that it sure looks like there is a space qualified Gemini solar filter there behind Don Pettit:


